Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography: An efficient tool for assessing thorium interaction with phosphorylated biomimetic peptides

Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1735, 25 October 2024, 465341: Fig. 1. Structure of the di-and tetra-phosphorylated cyclic peptides pS16 and pS1368 synthesized according to a biomimetic approach and typical pKas of glutamate and phosphoserine side chains.
The goal of this study is to investigate the interaction between thorium (Th⁴⁺), a surrogate for plutonium, and phosphorylated biomimetic peptides that mimic binding sites in osteopontin, a protein involved in actinide bioaccumulation. Using hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) coupled with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), the researchers aimed to separate, identify, and quantify Th–peptide complexes.
The study specifically evaluates the relative affinity of two peptides, pS16 and pS1368, for Th⁴⁺, and tests the selectivity of pS1368 in the presence of competing uranium (UO₂²⁺). Results reveal that Th⁴⁺ shows a strong preference for the tetra-phosphorylated peptide pS1368, even over its designed uranium target. This highlights the potential of HILIC-MS in advancing our understanding of actinide–biomolecule interactions relevant to nuclear toxicology and decorporation strategies.
The original article
Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography: An efficient tool for assessing thorium interaction with phosphorylated biomimetic peptides
Lana Abou-Zeid, Albert Pell, Marina Amaral Saraiva, Pascale Delangle, Carole Bresson
Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1735, 25 October 2024, 465341
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2024.465341
licensed under CC-BY 4.0
Selected sections from the article follow. Formats and hyperlinks were adapted from the original.
In previous works, we took advantage of HILIC to separate for the first time uranyl (UO22+) complexes with biomimetic peptides, of interest in nuclear toxicology [13,14]. Biomimetic approaches based on synthetic peptides as models of proteins are powerful to characterize protein's coordination sites responsible for the high affinity towards UO22+ and to better understand the toxicity mechanisms of this actinide (An) at the molecular scale [15]. These approaches are also highly relevant to provide primary molecular structures for the development of selective chelating agents for decorporation. Following this strategy, a series of multi-phosphorylated cyclic peptides has been synthesized to model the interaction sites of osteopontin (OPN), a hyper-phosphorylated target protein of UO22+ [[16], [17], [18], [19]] (Fig. 1).
 Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1735, 25 October 2024, 465341: Fig. 1. Structure of the di-and tetra-phosphorylated cyclic peptides pS16 and pS1368 synthesized according to a biomimetic approach and typical pKas of glutamate and phosphoserine side chains.
Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1735, 25 October 2024, 465341: Fig. 1. Structure of the di-and tetra-phosphorylated cyclic peptides pS16 and pS1368 synthesized according to a biomimetic approach and typical pKas of glutamate and phosphoserine side chains.
We also developed a dedicated analytical method based on the simultaneous coupling of HILIC to electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), to identify the separated complexes and determine simultaneously the selectivity and the affinity of the different biomimetic peptides towards UO22+. Furthermore, the selectivity of the peptide with the highest affinity (pS1368) towards UO22+ was determined in the presence of competing cations such as Cu2+, Zn2+ and Sr2+ by applying this new method [13,14].
In the present work, we extended the HILIC-ESI-MS/ICP-MS approach that we previously developed, to investigate the affinity of pS16/pS1368 phosphorylated peptides towards Th4+. This latter was selected as a Pu4+ analogue to carry out the studies in a conventional laboratory as both An are hard Lewis acids, display the same oxidation state and show high affinity for ligands containing hard donor atoms [21]. Moreover, the charge densities of Th4+ and Pu4+, expressed by the charge-to-ionic radius ratio, are in the same range: 3.8 e.Å−1 (Th4+) and 4.2 e.Å−1 (Pu4+) for the same coordination number (CN=8) [28]. The aim was also to evaluate the selectivity of the most powerful peptide, pS1368, towards Th4+ in presence of UO22+ as competing ion. The methodology was developed according to the following steps: i) evaluation of the selectivity of several polar HILIC stationary phases for separating Th4+-peptide complexes at physiological pH 7.4, reflecting relevant biological conditions in toxicology, ii) determination of the quantitative distribution of Th4+ among the pS16/pS1368 separated complexes owing to their simultaneous online identification and quantification, to assess the relative affinity of the two peptides for Th4+, iii) online determination of the quantitative distribution of Th4+ and UO22+ among the pS1368 complexes, to estimate the mutual influence of these An on their complexation properties and the selectivity of pS1368.
This study highlights the tremendous potential of HILIC to separate hydrophilic polar analytes such as An complexes, which are known for their complex chemistry and to be involved in electrostatic interactions upon coordination, rendering the task of their separation very difficult while preserving their integrity. This opens the door to a better knowledge of An behavior at the molecular scale, which is not generally achievable using separation modes commonly encountered in the literature. This is of prime concern in the field of nuclear toxicology, to better understand the An toxicity mechanisms and further develop specific decorporating agents.
2. Experimental part
2.3. Instrumentation
2.3.1. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography
Experiments were carried out using an ultimate 3000 UHPLC+ Dionex/Thermofisher scientific (Courtaboeuf, France), made of a degasser, a dual RS pump, an RS autosampler, a column compartment and an RS diode array detector. The columns used in this study are Acquity BEH Amide (150×2.1 mm; 1.7 µm, Waters), Acquity BEH HILIC (150×2.1 mm; 1.7 µm, Waters) and ZIC-HILIC (150×2.1 mm, 3.5 µm, Merck). The composition of the desired mobile phase was obtained by online mixing in the adequate proportions, solvent A (60/40 ACN/H2O v/v containing 20 mmol L−1 NH4CH3CO2) and solvent B (80/20 ACN/H2O v/v containing 20 mmol L−1 NH4CH3CO2).
For the quantification of pS16 and pS1368 in the stock solutions, an YMC Triart diol (100×2 mm; 1.9 μm) column was used with a mobile phase composed of 70/30 ACN/H2O v/v and 20 mmol L−1 NH4CH3CO2, eluting in isocratic mode at 300 μL min−1 and the injection volume was 3 μL.
2.3.2. Mass spectrometers
The used ESI mass spectrometers were a TSQ Quantum Ultra (Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Diego CA, USA) with a triple quadrupole mass analyzer (QqQ) and a LTQ Velos Pro (Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Diego CA USA) with a linear ion trap (LIT) analyzer. The ionization source of both mass spectrometers was equipped with an H-ESI-II probe. All mass spectra were recorded in negative ionization mode. For the sake of clarity, the Th4+and UO22+ complexes were denoted along the manuscript Th2(peptide)2 or UO2(peptide), by omitting the charge.
For the study of the complexes in solution by using the ESI-LIT-MS, the samples were continuously introduced into the source at a flow rate of 10 µL min−1. For the chromatographic experiments by coupling HILIC to ESI-QqQ-MS or ESI-LIT-MS, the flow introduced into the source was 300 µL.min−1. In all cases, the source parameters applied for each mass spectrometer are presented in Table 2.
The ICP-MS instrument was a single quadrupole XSeriesII (Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Diego, USA). The sample introduction system consisted of a perfluoroalkoxy PFA-ST nebulizer operating at 200 µL min−1 followed by a quartz cyclonic spray chamber thermostated at 3 °C (PC3 system from Elemental Scientific Instruments, Hoenheim, France). The simultaneous coupling of HILIC to ESI-QqQ-MS and ICP-MS was performed according to the setting up described in our previous work [30]. In order to prevent any carbon deposition due to the use of organic solvents, additional 8 mL min−1 oxygen flow rate was introduced in the plasma, through an “additional gas port” located in the spray chamber [31,32]. A platinum skimmer, a sampler cone and a 1 mm inner diameter injector were additionally used for this purpose. The chromatograms were recorded based on the signals of 232Th+, 238U+ and 209Bi+ with an integration time of 90 ms for each isotope.
3. Results and discussion
3.2. HILIC retention behavior of the Th4+-peptide complexes
In order to evaluate the impact of the phosphorylation degree of the peptides on their affinity for Th4+, the corresponding complexes must be first separated with a good selectivity and baseline resolution. Since Th-pS1368/Th-pS16 complexes are polar and charged, we investigated different chromatographic conditions in the aim of separating them at pH ∼ 7.4. This task was carried by coupling HILIC to ESI-LIT-MS, to identify each complex and their retention factor, following independent injections of the complexes into the column. The selectivity of non-grafted hybrid silica (BEH HILIC), amide (BEH amide) and zwitterionic-grafted (ZIC-HILIC) stationary phases was evaluated and the elution profiles of the complexes are overlaid in Fig. 3, for a mobile phase composed of 70/30 ACN/H2O v/v and 20 mmol L−1 NH4CH3CO2.
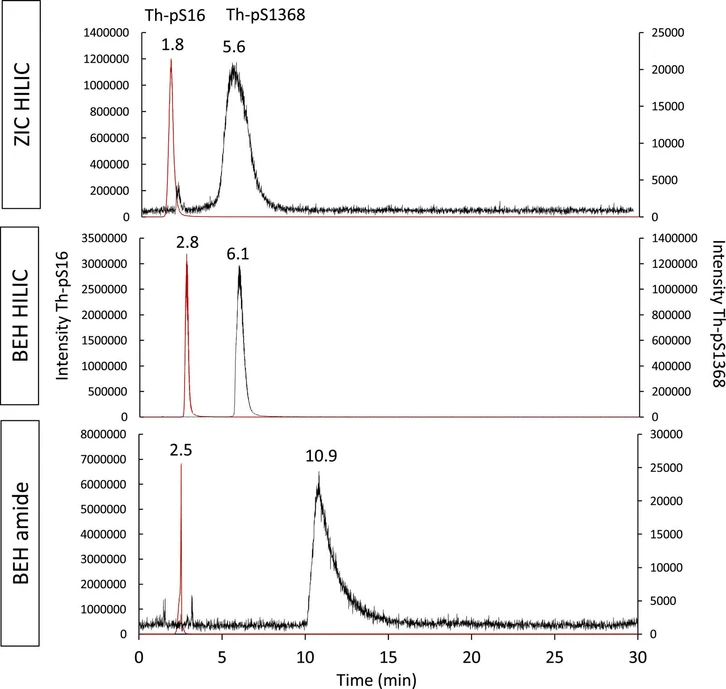 Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1735, 25 October 2024, 465341: Fig. 3. Overlay of the extracted ion current elution profiles of Th-pS16 (red) and pS1368 (black) complexes, acquired by ESI-LIT-MS, with m/z 1469–1470 and 1518–1520 for Th2pS162 and Th2pS13682, respectively. Samples: 1Th:2pS16 (Sample E) and 1Th:2pS1368 (Sample A). Columns: ZICsingle bondHILIC 150 × 2.1 mm, 3.5 μm, Acquity BEH HILIC 150 × 2.1 mm, 1.7 μm and Acquity BEH AMIDE 150 × 2.1 mm; 1.7 μm. In all cases, the mobile phase composition was 70/30 ACN/H2O v/v containing 20 mmol L−1 NH4CH3CO2, the flow rate was 300 μL min−1, the elution mode isocratic and Vinj = 3 μL.
Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1735, 25 October 2024, 465341: Fig. 3. Overlay of the extracted ion current elution profiles of Th-pS16 (red) and pS1368 (black) complexes, acquired by ESI-LIT-MS, with m/z 1469–1470 and 1518–1520 for Th2pS162 and Th2pS13682, respectively. Samples: 1Th:2pS16 (Sample E) and 1Th:2pS1368 (Sample A). Columns: ZICsingle bondHILIC 150 × 2.1 mm, 3.5 μm, Acquity BEH HILIC 150 × 2.1 mm, 1.7 μm and Acquity BEH AMIDE 150 × 2.1 mm; 1.7 μm. In all cases, the mobile phase composition was 70/30 ACN/H2O v/v containing 20 mmol L−1 NH4CH3CO2, the flow rate was 300 μL min−1, the elution mode isocratic and Vinj = 3 μL.
As shown in Fig. 3, the Th4+ complex of pS1368 is systematically more retained on the three columns than the pS16 complex, while this latter is poorly retained despite the differences in the polarity and charge of the grafted chemical groups. The retention factor of Th-pS16 complex displayed small changes, being 0.8, 1.5 and 1.8 for ZIC-HILIC, BEH amide and BEH HILIC, respectively. On the other hand, the retention factor of Th-pS1368 increased in the following order for the columns: ZIC-HILIC < Acquity BEH HILIC < Acquity BEH amide, being 4.7, 5.2 and 10, respectively.
The behavior of the Th-pS16 complex is quite puzzling since it exhibits globally a weak retention on the three columns. First of all, upon complexation with Th4+, the maximum overall charge of pS16 decreases from −5 to −2 for dimeric complex at neutral pH, leading to decreased retention according to the classical hydrophilic partitioning [34]. In addition, secondary electrostatic or hydrogen bonding interactions do not seem to participate significantly to the retention process, in particular for the ZIC-HILIC column, as Th-pS16 eluted close to the dead-time. These observations confirm the complexity of the HILIC retention mode and the challenge to predict a compound's behavior. Much mechanistic investigations still need to be done to understand the HILIC behaviour of metallic complexes, which will be useful in several fields of applications.
As mentioned previously, Th-pS1368 complex is more retained than Th-pS16 on the three columns, with retention factors higher than 4. This is in accordance with the higher polarity/charge of −10 for the dimeric complexes formed with the tetra-phosphorylated peptide pS1368 in comparison with those formed with the di-phosphorylated peptide pS16, as the former peptide displays two additional negatively charged phosphorylated groups in its scaffold. Moreover, pS1368 displays a negatively charged glutamate (Glu) in position 2 of the peptide scaffold, while pS16 contains a positively charged arginine (Arg) in the same position (see Fig. 1), which tends to further reduce the global negative charge of Th-pS16 complexes. This allows to suggest that the retention of Th-pS1368 complexes obey to hydrophilic partitioning as predominant mechanism, but additional hydrogen bonding interactions seem to take an important part, particularly for the Acquity BEH amide column as the retention factor increased by almost 2-fold in comparison with the other columns. These results are in line with what we previously observed when optimizing the HILIC separation conditions of a series of biomimetic peptides [34] and complexes of UO22+ and lanthanides containing different ligands [30,35,36], using several stationary phases.
Overall, Th4+ complexes of pS16 and pS1368 can be successfully separated using three stationary phases of different functionalization, with resolution factors of 7.8, 6.1 and 2.3 for BEH HILIC, BEH amide and ZIC-HILIC, respectively. The Acquity BEH HILIC column with a mobile phase composed of 70/30 ACN/H2O v/v and 20 mmol L−1 NH4CH3CO2 was then preferred for the rest of our study, as these are the best conditions to separate both complexes with the highest resolution factor and the most satisfying peak shapes. In these conditions, dimeric Th2(pS16)2 and Th2(pS1368)2 complexes were detected with the highest abundance, in agreement with the stoichiometry of the complexes observed by using direct injection mode. This also show that the dimeric structure of the complexes was preserved for both peptides through HILIC separation.
3.3. Determination of the relative affinity of the peptides towards Th4+ using HILIC-ESI-MS/ICP-MS
Like the other An, Th4+ exhibits high affinity for phosphate groups [37] and one promising decorporating agent of Th4+ recently described in the literature contain several phosphorylated functions [[38], [39], [40]]. Furthermore, the Th4+ interaction with OPN was demonstrated to be dominated by two oxgen atoms from phosphate groups binding to the An cation [41]. Therefore, the phosphorylation degree of the biomimetic peptides is expected to play a pivotal role in their affinity for Th4+. In order to evaluate the impact of this key parameter, several ratios of the di- and tetra-phosphorylated peptides, pS16 and pS1368, were added in a competing complexation reaction towards Th4+ (2Th:xpS16:ypS1368) at pH ∼ 7.4. The formed complexes were separated using HILIC, online identified by ESI-MS and simultaneously quantified by ICP-MS in a single step, following the method developed in our previous work [13]. The overlay of the chromatograms acquired by ICP-MS for samples A-E (Table 1) is presented in Fig. 4.
 Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1735, 25 October 2024, 465341: Fig. 4. Overlay of the chromatograms acquired by ICP-MS, recording the 232Th+ signal with an integration time of 90 ms for samples (A-E). 2Th:0pS16:3.4pS1368 (Sample A), 2Th:0.7pS16:3pS1368 (sample B), 2Th:1.5pS16:1.7pS1368 (sample C), 2Th:4.9pS16:0.7pS1368 (sample D), and 2Th:4pS16:0pS1368 (Sample E). Column: Acquity BEH HILIC 150 × 2.1 mm; 1.7 μm. Mobile phase: 70/30 ACN/H2O v/v containing 20 mmol L−1 NH4CH3CO2. Flow rate: 300 μL min−1, isocratic elution and Vinj: 3 μL. Each sample was injected in duplicate.
Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1735, 25 October 2024, 465341: Fig. 4. Overlay of the chromatograms acquired by ICP-MS, recording the 232Th+ signal with an integration time of 90 ms for samples (A-E). 2Th:0pS16:3.4pS1368 (Sample A), 2Th:0.7pS16:3pS1368 (sample B), 2Th:1.5pS16:1.7pS1368 (sample C), 2Th:4.9pS16:0.7pS1368 (sample D), and 2Th:4pS16:0pS1368 (Sample E). Column: Acquity BEH HILIC 150 × 2.1 mm; 1.7 μm. Mobile phase: 70/30 ACN/H2O v/v containing 20 mmol L−1 NH4CH3CO2. Flow rate: 300 μL min−1, isocratic elution and Vinj: 3 μL. Each sample was injected in duplicate.
As shown in Fig. 4, a single peak with a retention factor of 1.8 was detected when only pS16 was added to Th4+ (Sample E). By comparing this retention factor with the one obtained using ESI-MS, the peak was attributed to Th2(pS16)2. A peak tailing was observed, which could possibly be related to the formation of additional Th-containing species. Unfortunately, the extraction of the ESI mass spectrum from the tailing did not reveal the structural identity of this species. For samples A to C, containing excess or equal ratio of pS1368 relatively to pS16, only the peak of Th2(pS1368)2, attributed owing to ESI-MS, was detected (Fig. 4). This means that even when pS16 is present in equivalent ratio as pS1368, it does not displace pS1368 from Th2(pS1368)2, which strongly supports a higher affinity of pS1368 towards Th4+ with respect to pS16. Furthermore, when pS16 is in excess in comparison with pS1368 (Sample D), two peaks were observed in addition to those corresponding to Th2(pS16)2 and Th2(pS1368)2. The peak with a retention factor of 2.8 was attributed to a ternary binuclear complex Th2(pS16)(pS1368), after matching its retention factor with this of the peak detected by ESI-MS, while the remaining peak eluting at k = 3.5 could not be attributed. The occurrence of this ternary complex is in accordance with a previously published work, reporting Th4+ ternary binuclear complex formed with Transferrin (Tf) and an iron biding siderophore Deferoxamine (DFOB), as Th2(Tf)(DFOB) [27].
4. Conclusion
The HILIC-based approach that we developed allowed to evaluate the relative affinity and selectivity of biomimetic peptides towards An, which is of prime importance to better understand the key parameters driving they coordination with target biomolecules in vivo or decorporating agents based on chelation. In particular, the simultaneous coupling of HILIC to ESI-MS and ICP-MS was applied to separate, identify and quantify Th4+ complexes containing di-and tetra-phosphorylated cyclic peptides, pS16 and pS1368. The selectivity of several stationary phases was assessed and the Acquity BEH HILIC column with a mobile phase composed of 70/30 ACN/H2O v/v and 20 mmol L−1 NH4CH3CO2 yielded the best separation of the newly identified dimeric complexes Th2(pS16)2 and Th2(pS1368)2. The quantitative distribution of Th4+ among the separated complexes was determined online and in a single step, showing that the tetra-phosphorylated peptide pS1368 exhibits stronger affinity for Th4+ than the di-phosphorylated one, pS16. The addition of equimolar ratios of pS16 and pS1368 to Th4+ led to the formation of only the pS1386-containing complex, while only 19 % of Th2(pS16)2 was formed when pS16 was seven times in excess compared to pS1368, confirming this result. Finally, through the same approach, the relative affinity and selectivity of pS1368 for the two An cations Th4+ and UO22+ was assessed online. Interestingly, this peptide initially designed to promote UO22+ coordination in the equatorial plane, binds even more efficiently the spherical Th4+ cation, probably because of the ability of this latter to form dimeric species, which fulfils the coordination requirement of this An(IV) ion.
The ongoing development of HILIC stationary phases with decreased dimensions and/or core shell particles, sub-2 µm diameter particles and monolithic materials, offers the opportunity to get further insight into the separation of An species based on this separation mode, while decreasing the consumption of the sample and the waste production. This point is of high concern while dealing with radioelements and highly toxic metals.