A novel LC-TQ-MS/MS method for quantifying mefenamic acid-NDSRI (N-nitroso drug substance-related impurity) in mefenamic acid tablet and pediatric suspension dosage forms: a comparative study with a cost-effective white, green, and blue UPLC method
RSC Advances, Volume 15, Issue 3, 2025, 1957-1969: Graphical abstract
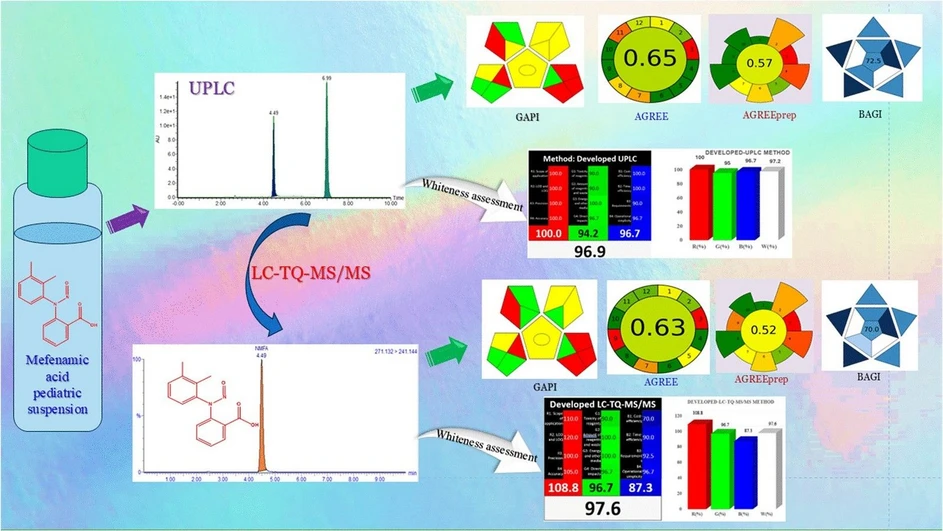
This study presents novel LC-TQ-MS/MS and cost-effective UPLC methods for quantifying N-nitroso drug substance-related impurity (N-MFA) in mefenamic acid tablets and pediatric suspensions. Both methods were successfully validated according to ICH guidelines, demonstrating excellent sensitivity, linearity, and accuracy. LC-MS/MS achieved quantification at 0.01 ng/mL (1 mg/mL MFA), while UPLC quantified down to 0.036 μg/mL (10 mg/mL MFA). Linearity was confirmed across 0.01–125 ppm for LC-MS/MS and 3.6–125 ppm for UPLC with R² = 0.999.
Accuracy recoveries ranged from 90.43% to 101.34% for LC-MS/MS and 92.12% to 101.21% for UPLC. Both methods were applied to commercial formulations and demonstrated suitability for routine use in R&D and quality control labs. Additionally, sustainability and environmental impact were evaluated using tools like GAPI, AGREE, and RGB12, confirming their green analytical profile.
The original article
A novel LC-TQ-MS/MS method for quantifying mefenamic acid-NDSRI (N-nitroso drug substance-related impurity) in mefenamic acid tablet and pediatric suspension dosage forms: a comparative study with a cost-effective white, green, and blue UPLC method
Srinivas Nakka, Naresh Kumar Katari, Siva Krishna Muchakayala, Sreekantha Babu Jonnalagadda, Surendra Babu Manabolu Surya
RSC Advances, Volume 15, Issue 3, 2025, 1957-1969
https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ra08425j
licensed under CC-BY 3.0
Selected sections from the article follow. Formats and hyperlinks were adapted from the original.
Regulatory agencies have underscored the significance of predicting toxicity and precisely measuring the levels of nitrosamine contaminants in certain pharmaceuticals. These impurities, which include nitrosamines derived from active pharmaceutical ingredients, are referred to as Nitrosamine Drug Substance Related Impurities (NDSRIs). Nitrosamines, or N-nitrosamines, are molecules characterized by their N-nitroso functional group. They are classified as a group of concern due to their status as human carcinogens, with evidence showing that long-term intake above acceptable levels can increase cancer risks.
These NDSRI substances are categorized into one of three “Cohort-of-Concern” (CoC) groups: aflatoxin-like, alkyl-azoxy, and N-nitroso. “CoC” denotes a collection of highly potent mutagenic compounds requiring special attention due to potential health risks. The focus of pharmaceutical regulatory authorities has shifted from common nitrosamines to NDSRIs because of their potential carcinogenicity and their presence in drug products at unacceptable levels.1–6 As a result, regulatory authorities recalled various drug products worldwide. Furthermore, the detection and quantification of NDSRIs are of significant concern to analytical researchers.7–11
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a class of medications that relieve pain and inflammation, including in renal transplants and chronic non-cancer pain in children.12,13 About 30 million people worldwide use NSAIDs every day, according to a report by Medical News Today. The worldwide market for NSAIDs was valued at USD 15.58 billion in 2019 and is envisioned to reach USD 24.35 billion by 2027.
Mefenamic acid (MFA) is chemically known as 2-[(2,3-dimethylphenyl)amino]benzoic acid, with the chemical formula C15H15NO2 and a molecular weight of 241.28 g mol−1. MFA is classified as an anthranilic acid (phenolate) NSAID that exhibits both antipyretic and analgesic properties. This medication treats moderate pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis, post-operative pain, menstrual pain, rheumatoid arthritis, toothaches, and severe back and muscle pain. Additionally, it is also used to manage menorrhagia.14,15
To our knowledge, this is the first UPLC-MS/MS and environmentally friendly UPLC method for quantifying the target compound N-MFA. As a result, there are no existing methods available to compare with the proposed UPLC-TQ-MS/MS and the cost-effective green UPLC method. Various regulatory agencies, including the US FDA and Health Canada, have proposed that the acceptable intake (AI) value for N-MFA is 78 000 ng per day.16,17 The interim control limit for N-MFA is 62.4 ppm, which can be derived from the AI value of the impurity and the maximum daily dose of the MFA. Hence, simple and highly sensitive UPLC-MS/MS and UPLC methods have been developed for the accurate quantification of N-MFA in MFA drug formulations, including tablets and pediatric suspensions.
The current study aimed to assess genotoxicity using (Q)-SAR (Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship) models and to develop new LC-TQ-MS/MS and UPLC methods for quantifying N-MFA in both the MFA drug substance and its formulation dosage forms. Recent regulatory guidelines demonstrate that setting the quantitation limit (QL) at 30% is considered reasonably good and acceptable. If the values consistently fall below the QL across all process validation batches and corresponding stability samples (both accelerated and long-term), it is acceptable to proceed with skip lot testing. UPLC can detect the N-MFA impurity below the 30% control limit (∼19 ppm). Therefore, this cost-effective UPLC method is proposed alongside the LC-TQD-MS/MS for use in quality control laboratories. Both methods have been successfully validated regarding the QL, linearity, precision, accuracy, and robustness. The sustainability and eco-friendliness of the UPLC method were evaluated using greenness and whiteness assessment metrics, including GAPI, the analytical eco-scale, AGREE, AGREEprep, BAGI, and RGB12 tools.18–20 The results indicated that the proposed method exhibits a high level of greenness and whiteness. Fig. 1 illustrates the chemical structures of MFA, N-DPA (N-nitroso diphenylamine), and N-MFA. The applicability of these methods was successfully verified through the analysis of commercial samples of APIs and dosage forms of MFA.
Materials and method
Instrument and software
The chromatographic investigation was accomplished on the Waters H class UPLC system, which includes a PDA-photo diode array detector model (L20UPD127A) modules, an Auto Sampler Manager with a Flow-Through Needle (FTN-L20FTP352G), Quaternary Solvent Manager (QSM-L20QSP358A) (Waters Corporation, USA). For the LC-TQ-MS/MS method (MRM analysis) a Waters Xevo TQ-XS MS system equipped with an ESI ion source was utilized. A Mettler-Toledo (Model: XPE205, Columbus, Ohio, USA) analytical balance was employed to weigh the samples and the impurity standard. The analysis utilized high-purity water obtained from the Millipore Milli-Q purification system (Bedford, MA, USA). Centrifuge (Model: 5810R, Hemburg, Germany) from Eppendorf. ChemDraw Professional 15.0 sketched MFA, N-DPA, and N-MFA molecular structures. The two primary (Q)-SAR methodologies employed were the Derek Nexus (version 6.2.0, featuring the Derek KB 2022 1.0 knowledge base) and the Sarah Nexus (version 3.2.0, which includes the Nexus version 1.9 and the Sarah Model 2022.1). Target Lynx software v 4.2 was used to compute all LC-TQ-MS/MS acquisition and process parameters.
Results and discussion
Development and optimization of mass spectrometry conditions
To develop an accurate quantification of N-MFA in MFA tablets and pediatric suspensions, optimizing mass parameters is a decisive step. We intended to attain a sensitive, precise, and accurate method. For N-MFA quantification, the MRM technique was utilized. For initial mass conditions optimization by injecting the 1000 ng mL−1 concentration of N-MFA into mass spectrometry using infusion mode to identify the prominent product ion in electron spray ionization in positive ion mode (m/z 271.13 → 241.14). Due to the pump flow rate being set at 0.7 mL min−1 and the recommended desolvation gas temperature and gas flow being 450 °C and 900 L per Hr, hence performed the analysis with the values mentioned earlier. Employing the Intellistart software, which is built into Waters mass lynx software, to fine-tune MS/MS parameters, including cone voltage, capillary voltage, and collision energy values with different mass transitions. Intellistart identified three major MRM transitions, including m/z 271.13 → 241.14, m/z 271.13 → 223.12, and m/z 271.13 → 208.10 (Fig. 2). After careful optimization of cone voltage and collision energies finalized, the quantifier ion transition as m/z 271.13 → 241.14 and the qualifier ion transition as m/z 271.13 → 223.12 (Fig. S4†). A mass spectrometer was installed, a 50 μL loop, which improves the peak shape when injecting the samples containing a high percentage of organic solvents. The highest intensity of quantifier and qualifier ions are detected by using the below MS/MS optimized conditions: cone voltage is 18 V, capillary voltage is 2.48 kV, collision energy is 8 V and 18 V for qualifier and quantifier respectively, desolvation gas temperature is 450 °C, and gas flow 900 L h−1. In the MS/MS method, the events program flow state was directed from 0 to 5.4 min set to mass to detect the N-MFA and the flow state from 5.5 to 10 minutes to avoid the high concentration of MFA contamination triggered by formulation tablet and pediatric suspension samples 1 mg mL−1 concentration. The optimized MS/MS parameters are shown in Table 2.
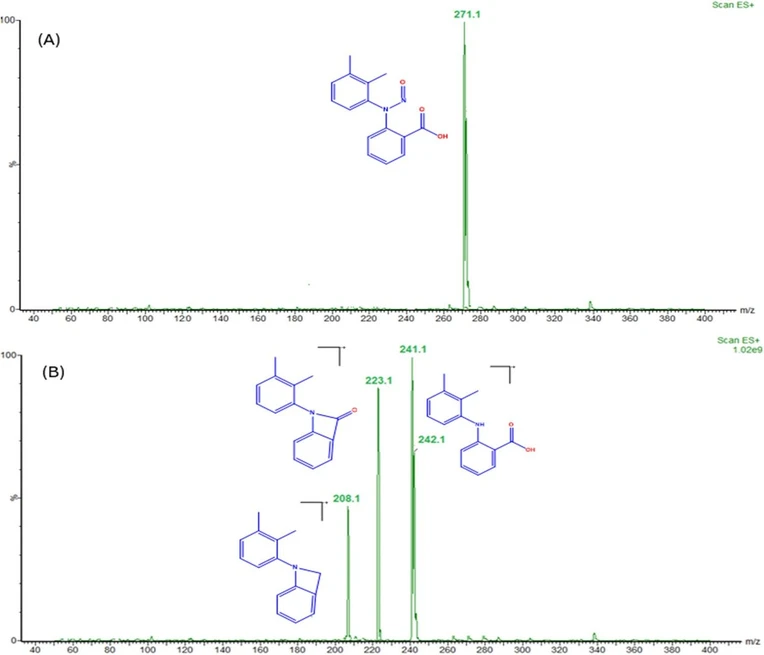 RSC Advances, Volume 15, Issue 3, 2025, Pages 1957-1969: Fig. 2. (A) Mass spectrum of NMFA, and (B) MS/MS fragmentation pattern of N-MFA.
RSC Advances, Volume 15, Issue 3, 2025, Pages 1957-1969: Fig. 2. (A) Mass spectrum of NMFA, and (B) MS/MS fragmentation pattern of N-MFA.
Method validation
The present proposed LC-TQ-MS/MS and UPLC methods have been fully validated by ICH Q2R2, USP 〈1225〉 guidelines,23 and published journals,24–26 following the method validation parameters, such as specificity, limit of detection, limit of quantitation, linearity, precision, accuracy, robustness, and solution stability. Table 3 presents the results of the validation study, demonstrating that the method is specific, precise, linear, and accurate.
Specificity
The current analytical method's specificity is demonstrated by the liquid chromatography system's capability to differentiate between the diluent, placebo, MFA, N-MFA, and N-MFA spiked at the specification level. Injected each 10 μL for LC-MS/MS and 50 μL for UPLC of diluent, placebo, N-MFA standard solution, and sample solution of MFA. The analysis showed that no co-eluting peaks were apparent at the retention time (tR) of N-MFA, allowing for the specific and accurate estimation of N-MFA in MFA tablet and pediatric suspension formulations. Overlay UV spectra of N-MFA and MFA are shown in Fig. S4,† and the typical LC-MS/MS and UPLC chromatograms indicating the specificity of the method can be found in Fig. 3 and 4, respectively.
 RSC Advances, Volume 15, Issue 3, 2025, Pages 1957-1969: Fig. 3. Typical MRM chromatograms of (A) placebo, (B) N-MFA standard at the specification level, and (C) UV spectra of N-MFA spiked to the MFA sample at the specification level, and (D) MRM of N-MFA spiked to the MFA sample at the specification level.
RSC Advances, Volume 15, Issue 3, 2025, Pages 1957-1969: Fig. 3. Typical MRM chromatograms of (A) placebo, (B) N-MFA standard at the specification level, and (C) UV spectra of N-MFA spiked to the MFA sample at the specification level, and (D) MRM of N-MFA spiked to the MFA sample at the specification level.
 RSC Advances, Volume 15, Issue 3, 2025, Pages 1957-1969: Fig. 4. Typical chromatograms of (A) blank, (B) placebo, (C) N-MFA standard at specification level, and (D) N-MFA spiked to the MFA sample at specification level.
RSC Advances, Volume 15, Issue 3, 2025, Pages 1957-1969: Fig. 4. Typical chromatograms of (A) blank, (B) placebo, (C) N-MFA standard at specification level, and (D) N-MFA spiked to the MFA sample at specification level.
Conclusion
In conclusion, two interdependent (Q)-SAR tools were utilized to assess and classify N-MFA as a Class-3 category, designated as a “CoC” which suggests potential genotoxicity. Diphenylamine is a precursor that can lead to the formation of N-MFA. The acceptable intake (AI) of N-MFA was derived from N-DPA, and the determined AI for N-MFA is 78 000 ng; hence the specification limit is 62.4 ppm. Proposed novel LC-TQ-MS/MS and cost-effective UPLC methods are proposed to accurately quantify N-nitroso mefenamic acid (N-MFA) in mefenamic acid (MFA) tablets and pediatric suspension dosage forms. The proposed method has been successfully validated in compliance with ICH guidelines. The developed methods were further applied to commercially available mefenamic acid formulations to determine accurate and precise quantification of N-MFA. For routine quality control laboratories, this cost-effective UPLC method can be used to detect 30% of the interim control limit (∼19 ppm). Furthermore, sustainability and eco-friendliness were evaluated using greenness and whiteness assessment metrics, including the analytical eco-scale, GAPI, AGREE, AGREEprep, BAGI, and RGB12 tools. The results indicated that the method proposed exhibits a high level of greenness and whiteness. Both methods can be used to determine N-MFA content in mefenamic acid formulation dosage based on the availability of instruments LC-TQ-MS/MS and UPLC in R&D and quality control laboratories.