A facile and eco-friendly simultaneous quantification LC-TQ-MS/MS approach for N-Nitroso Moxifloxacin and di-nitroso pyrrolopiperidine in Moxifloxacin tablets and eye drops
Green Analytical Chemistry, Volume 12, 2025, 100188: Graphical abstract
This study presents a novel and eco-friendly LC-QqQ-MS/MS method for the trace-level quantification of N-Nitroso Moxifloxacin (N-MOX) and di-Nitroso pyrrolopiperidine (DNPP) in moxifloxacin drug substances and products. As both NDSRIs fall into potency category 4 with an acceptable intake limit of 1500 ng/day, their control is vital for patient safety. The method achieves efficient chromatographic separation using a Cortecs T3 C18 column and gradient elution, and employs MRM transitions m/z 431.0 → 386.0 for N-MOX and 185.1 → 138.1 for DNPP.
Validated per ICH guidelines, the method proved accurate, sensitive, and reproducible. Green assessment tools confirmed its low environmental impact in terms of time, solvent use, waste, and sample volume. Successfully applied to commercial moxifloxacin tablets and eye drops, this method offers a robust solution for routine NDSRI monitoring in pharmaceuticals.
The original article
A facile and eco-friendly simultaneous quantification LC-TQ-MS/MS approach for N-Nitroso Moxifloxacin and di-nitroso pyrrolopiperidine in Moxifloxacin tablets and eye drops
Srinivas Nakka, Siva Krishna Muchakayala, Surendra Babu Manabolu Surya
Green Analytical Chemistry, Volume 12, 2025, 100188
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.greeac.2024.100188
licensed under CC-BY 4.0
Selected sections from the article follow. Formats and hyperlinks were adapted from the original.
The emergence of nitrosamine impurities in active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) is a complex issue influenced by various factors related to chemical synthesis, raw material quality, and manufacturing processes. The concern of nitrosamine contamination in pharmaceuticals is quickly becoming more widespread, extending not only beyond smaller nitrosamines but also nitrosamine drug substance-related impurities (NDSRIs). These NDSRIs are particularly challenging because they are structurally related to the API, making their presence almost unavoidable [[1], [2], [3], [4]]. Moreover, the lack of carcinogenicity or mutagenicity data for most NDSRIs complicates the establishment of acceptable intake levels (AIs). Based on the GSRS (Global Substance Registration System) database, 41.4 % of APIs and 30.2 % of API impurities are potential nitrosamine precursors. However, when tertiary amines are excluded from this classification, the percentages adjust to 14.7 %, and 12.8 % are for APIs and API impurities, respectively, that could potentially lead to nitrosamine formation [5].
In July 2023, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) introduced a novel assessment method known as the Carcinogenic Potency Categorization Approach (CPCA) for N-nitrosamines. This approach was designed to facilitate the determination of AI for nitrosamines, thereby simplifying the complexities associated with setting AI [6,7]. Developing an analytical method with high sensitivity for regular analysis presents a considerable challenge, given the outstandingly low acceptable intake thresholds for these impurities and is fraught with sensitivity issues, while reactivity and stability concerns further complicate the analysis.
Moxifloxacin (MOX) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that acts against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria's from the fourth-generation fluoroquinolone class of medication and is prescribed for numerous bacterial ailments such as pneumonia, conjunctivitis, endocarditis, tuberculosis, and sinusitis. It can be administered orally, intravenously, or as eye drops. It obstructs the bacteria's DNA replication process, vital for their growth and proliferation [[8], [9], [10]]. It is acknowledged worldwide for its efficacy in treating numerous bacterial infections and is listed among the World Health Organization (WHO)’s essential medicines.
Green analytical chemistry (GAC) is dedicated to developing and applying methods that minimize environmental impact and improve sustainability. The core goal of this approach is to reduce the use of hazardous substances, minimize waste production, and encourage energy-efficient analytical processes. In 1998, Paul Anastas and his team introduced twelve principles to assess the environmental impact of chemical processes, which were later adapted for analytical methods [11]. Gałuszka et al. developed twelve principles specifically for green analytical chemistry, incorporating the core concepts of green chemistry [12]. It involves analyzing smaller sample quantities and reducing the usage or volume of toxic reagents, solvents, and energy consumption. Experts in green chemistry focus on the use of safe, environmentally friendly chemicals and low-waste assessment methods [[13], [14]].
A comprehensive literature review reveals that, to date, there are no published research articles on the simultaneous trace-level quantification of N-MOX (1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-((4aS,7aS)-1-nitrosooctahydro-6H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid), and DNPP {(4aS,7aS)-1,6-dinitrosooctahydro-1H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine}. The current study aimed to assess genotoxicity by utilizing Quantitative structure-activity relationship ((Q)-SAR) models that apply carcinogenic potency category classification, while also developing a straightforward, rapid, and novel UPLC-triple quadrupole (QqQ)-MS/MS method for the simultaneous trace-level quantification of N-MOX and DNPP impurities. The MOX, N-MOX, and DNPP chemical structures are illustrated in Fig. 1.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Instruments and software
The chromatographic study was performed on the Waters H class UPLC (Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography) system, which includes a PDA-photo diode array detector model (L20UPD127A) modules, an Auto Sampler Manager with a Flow-Through Needle (FTN- L20FTP352G), Quaternary Solvent Manager (QSM- L20QSP358A) (Waters Corporation, USA). A Waters Xevo TQ-XS LC-MS system equipped with a triple quadrupole (QqQ) mass analyzer and Electrospray Ionization (ESI) ion source with multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) techniques was utilized (Waters Corporation, Milford, Massachusetts, USA). A Mettler-Toledo (Model: XPE205, Columbus, Ohio, USA) analytical balance was employed to weigh the samples and the impurity standard. The analysis utilized high-purity water consists of resistivity <18.2 MΩ˙cm at 25 °C, TOC (Total Oxidizable Carbon) ≤5 ppb, Bacteria <10 CFU (Colony-forming unit) / 100 mL obtained from the Millipore Milli-Q purification system (Bedford, MA, USA). Centrifuge (Model: 5810R, Hemburg, Germany) from Eppendorf. Millex-GV hydrophilic 0.22 µm PVDF filters (Burlington, Massachusetts, USA) have been obtained from Millipore. Using ChemDraw Professional 15.0, sketched the chemical structures of MOX, N-MOX, and DNPP. The two primary (Q)-SAR methodologies employed were the Derek Nexus (version 6.2.0, featuring the Derek KB 2022 1.0 knowledge base) and the Sarah Nexus (version 3.2.0, which includes the Nexus version 1.9 and the Sarah Model 2022.1). MassLynx and TargetLynx software (v 4.2) were used for all LC-QqQ-MS/MS acquisition parameters and to process the data, respectively.
3. Results and discussion
3.4. Development and optimization of MS/MS conditions
Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM) is an analytical method of high sensitivity and specificity, gaining prominence in different fields, including drug development, clinical research, and metabolomics [17]. It enables precise detection and accurate quantification of impurities at very low concentrations. During the current study, N-MOX and DNPP impurities were detected and quantified using the MRM approach in an electrospray ionization positive mode (ESI). The capillary voltage (kV), desolvation temperature ( °C), and desolvation gas flow (L/Hr) are the three major ESI source parameters. Concerning the low pump flow rate of 0.3 mL/min, the recommended desolvation gas temperature and gas flow are 450 °C and 900 L/Hr. Both N-MOX and DNPP showed maximum intensity at a capillary voltage of 3.0 kV. The MS parameters for MRM channels, such as collision energy (CE) and cone voltage (CV), were individually optimized to ensure a stable and robust signal for the compounds. Intellistart software, built into Waters mass lynx software, is employed to fine-tune MS/MS parameters, including cone voltage and collision energy values with different mass transitions. MS/MS fragmentation pattern for both impurities shown in Fig. 3. After careful optimization of cone voltage and collision energies finalized, the quantifier ion transition as m/z 185.1→ 138.1 and the qualifier ion transition as m/z 185.1 → 96.10 for DNPP; the quantifier ion transition as m/z 431→ 386 and the qualifier ion transition as m/z 431 → 319 for N-MOX (Fig. S2). A mass spectrometer, a 50 µL loop, was installed, which improves the peak shape when injecting samples containing a high percentage of organic solvents. Later, studies of the impact of collision energies varying from 5 to 30 V and optimized collision energy for N-MOX and DNPP were 20 and 15 V, respectively (Fig. S3). The MRM quantifier qualifier and ESI source parameters for both impurities were tabulated in Table 2. In the MS/MS method; the events program was configured to direct the flow from 0 to 2.8 min. for mass detection of DNPP. To prevent contamination from high concentrations of MOX from tablets and eye drops (5 mg/mL concentration), the flow was diverted to waste from 2.9 to 4.5 min. From 4.6 to 8 min, the flow was directed again to detect N-MOX.
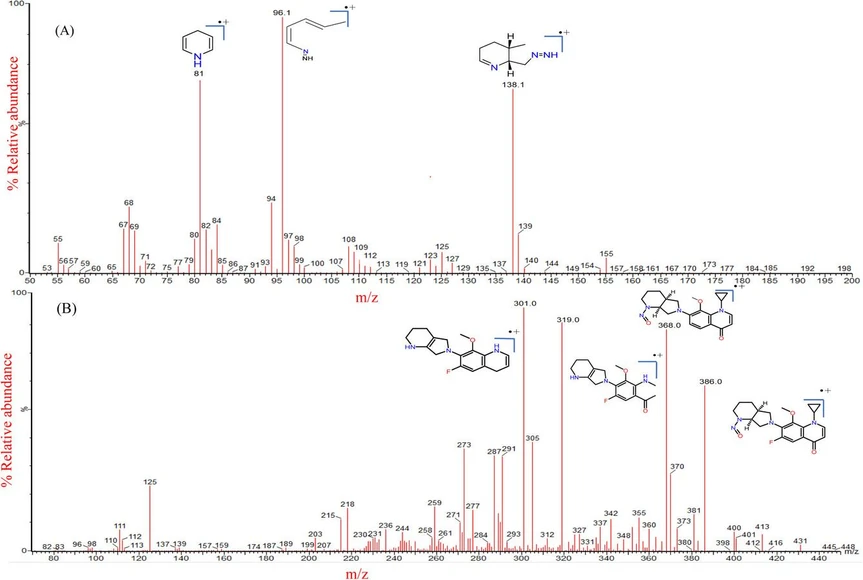 Green Analytical Chemistry, Volume 12, 2025, 100188: Fig. 3. MS/MS fragmentation pattern for (A) DNPP, and (B) N-MOX.
Green Analytical Chemistry, Volume 12, 2025, 100188: Fig. 3. MS/MS fragmentation pattern for (A) DNPP, and (B) N-MOX.
3.9. Method greenness assessment of the proposed method
The environmental impact or “greenness” of the recently developed LC-QqQ-MS/MS method was evaluated using insights from published journals [[24], [25], [26]] and contemporary tools, including the Analytical Eco-scale, GAPI, AGREE, AGREEprep, and the Blue Applicability Grade Index (BAGI).
3.9.2. Green analytical procedure index (GAPI) assessment tool
In 2018, Płotka-Wasylka introduced the GAPI [28], which uses a pictogram with red, yellow, and green colors to represent high, medium, and low environmental impacts, respectively. For the developed LC-QqQ-MS/MS method, pictograms 2, 3, 6, 8, 9, and 12 are green, indicating low environmental impact. Pictograms 4, 5, 10, 11, and 14 are yellow, reflecting medium impact, while pictograms 1, 7, 13, and 15 are red, indicating high impact. This visual representation highlights both qualitative and quantitative environmental impacts [29]. An illustration of the GAPI pictogram is provided in Fig. 7A. Table 6 details the principles of GAPI, the selected method condition values, and their corresponding scores.
 Green Analytical Chemistry, Volume 12, 2025, 100188: Fig. 7. Pictograms of (A) GAPI (B) AGREE, (C) AGREEprep, and (D) BAGI.
Green Analytical Chemistry, Volume 12, 2025, 100188: Fig. 7. Pictograms of (A) GAPI (B) AGREE, (C) AGREEprep, and (D) BAGI.
4. Conclusion
A novel, highly sensitive, and eco-friendly UPLC-QqQ-MS/MS method has been developed for the simultaneous trace-level quantification of MOX NDSRI and DNPP in MOX drug substances, tablets, and eye drops. The method was rigorously validated according to ICH Q2(R2) guidelines, including parameters such as linearity, LOD, LOQ, accuracy, precision, and robustness, showing excellent performance with high recovery rates and lower % RSD values and detecting N-MOX from 0.1 ng/mL to 37.5 ng/mL and DNPP from 0.5 ng/mL to 37.5 ng/mL. The method's versatility and sensitivity were demonstrated through a successful application to the analysis of commercial MOX tablets and eye drops, thereby ensuring the safety of MOX formulations. Furthermore, the proposed LC-QqQ-MS/MS method was evaluated using advanced green tools such as Analytical Eco-scale, GAPI, AGREE, AGREEprep, and BAGI, which confirmed its sustainability. This method can be employed for the accurate trace-level quantification of N-MOX and DNPP in any of the drug substances and formulations adopting suitable sample preparation. This methodology offers several advantages, such as reduced sample and organic solvent consumption, as well as a shorter run time, allowing for the processing of more batch samples. Overall, this validated UPLC-QqQ-MS/MS method presents a precise, reliable, and environmentally friendly approach for the simultaneous quantification of N-MOX and DNPP, offering a valuable contribution to pharmaceutical research and development.




