News from LabRulezLCMS Library - Week 13, 2025
LabRulez: News from LabRulezLCMS Library - Week 13, 2025
Our Library never stops expanding. What are the most recent contributions to LabRulezLCMS Library in the week of 24thMarch 2025? Check out new documents from the field of liquid phase, especially HPLC and LC/MS techniques!
👉 SEARCH THE LARGEST REPOSITORY OF DOCUMENTS ABOUT LCMS AND RELATED TECHNIQUES
👉 Need info about different analytical techniques? Peek into LabRulezGCMS or LabRulezICPMS libraries.
This week we bring you application notes by Agilent Technologies, Knauer, Mestrelab Research, Shimadzu and Waters Corporation and technical note by Thermo Fisher Scientific!
1. Agilent Technologies: USP Method Transfer from an Agilent 1100 Series Quaternary LC to an Agilent 1260 Infinity III LC
Proof of equivalency and transfer to UHPLC conditions
- Application note
- Full PDF for download
The USP and other pharmacopoeias provide validated methods for the analysis of many pharmaceuticals. For validated methods in the pharmaceutical industry, method transferability is compulsory, and the transfer of analytical procedures from one laboratory to another requires comparative testing.1 One example of instrument-to-instrument method transfer is the transfer of conventional LC methods from legacy equipment to new instruments, such as the 1260 Infinity III LC System. Each method must be verified under actual conditions of use when applied to new instruments for the first time2 , typically by determination of system suitability criteria that must be met. This application note shows the analysis of related compounds of abacavir according to the USP monograph3 , using an 1100 Series Quaternary LC System. It has previously been shown that conventional LC methods can be transferred seamlessly from an 1100 Series Quaternary LC to a 1260 Infinity III LC.4 Here, the seamless transfer of a USP monograph method from the 1100 Series Quaternary LC to the 1260 Infinity III LC is shown for the analysis of related compounds of abacavir. Furthermore, the analysis of related compounds of abacavir is translated to UHPLC conditions within the permitted adjustments of chromatographic conditions in gradient elution LC, described in USP chapter 621.5 The transfer to UHPLC conditions facilitates shorter analysis times and lower solvent consumption while maintaining separation performance, thereby reducing the cost per sample.
Results and discussion
Before starting the analysis of related compounds of abacavir, a performance check of the 1100 Series Quaternary LC and the 1260 Infinity III LC was performed by analysis of the InfinityLab LC Performance Standard. Excellent results were obtained in terms of peak shape as well as retention time and peak area precision (data not shown), demonstrating that performance of both LC systems was suitable for analysis.
The analysis of related compounds of abacavir according to the USP monograph3 prescribes the use of a 3.9 × 150 mm, 5 µm packing L1 column and the method parameters shown in Table 1. For the assessment of system suitability, a 0.25 mg/mL solution of the USP abacavir related compounds mixture (system suitability solution) needs to be analyzed and the resolution between abacavir and trans-abacavir must be at least 1.5.
The USP monograph method is translated to a more common 4.6 × 150 mm, 5 µm column following the procedures described in USP chapter 6215 , which results in an adjustment of flow rate and injection volume (Table 2).
Figure 1 shows the analysis of the abacavir related compound mixture employing the 1100 Series Quaternary LC and the method parameters described in Table 2. The resolution between abacavir and trans-abacavir was 2.6. Therefore, the analysis fulfilled the system suitability criteria.
The analysis of related compounds of abacavir using the method parameters described in Table 2 were transferred to the 1260 Infinity III LC (Figure 2). Excellent results were obtained in terms of retention time precision, leading to high trust in the data. The resolution between abacavir and trans abacavir was 2.6, which fulfilled the system suitability criteria.
Conclusion
The analysis of related compounds of abacavir according to the USP monograph can seamlessly be transferred from an Agilent 1100 Series Quaternary LC to an Agilent 1260 Infinity III LC. Employing the 1260 Infinity III LC, the method can also be translated to UHPLC conditions using an Agilent InfinityLab Poroshell 120 column, enabling significant reductions in analysis time and solvent consumption, thereby reducing the cost per sample.
2. KNAUER: Determination of mono- and polyaromatic hydrocarbons in diesel fuels with AZURA® Analytical HPLC system using RI detection
- Application note
- Full PDF for download
It is well known that the best performance and maximum lifetime of an engine can be reached, when the amount of aromatic hydrocarbons in diesel and aviation turbine fuels is as low as possible. Since the aromatic hydrocarbon content can affect the cetane number of fuels and cause emissions due to incomplete burning, there are different regulations to protect the environment and public health. Below, we describe a method according to DIN EN 12916 [1] for the the determination of mono- and polyaromatic hydrocarbons, like 1,2-dimethylbenzene, fluorene, and phenanthrene in diesel fuel samples.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
For the analysis of mono-, and polyaromatic hydrocarbons we used the following HPLC system setup: isocratic AZURA P6.1L pump with 10 mL pump head, AZURA AS 6.1L autosampler, AZURA RID 2.1L detector and AZURA CT 2.1L thermostat. The separation was performed on normal phase column ZORBAX®, NH2 250 x 4.6 mm. The used mobile phase was n-heptane. For calibration three concentration levels were used. The amounts of 1,2-dimethylbenzene, fluorene and phenanthrene in corresponding solutions A, C and D are presented in Tab. 1. The samples from the respective diesel fuel batches were diluted to 10 % with n-Heptan and analyzed.
CONCLUSION
This application demonstrates, that the AZURA® isocratic analytical HPLC system in combination with AZURA RID 2.1L detector suitable for determining of mono- and polyaromatic hydrocarbons in diesel fuel according to DIN EN 12916.
3. Mestrelab Research: Reaction, reactions, reactions - data automation to the rescue!
- Application note
- Full PDF for download
Computational chemistry and AI have allowed us to make great strides in predicting reaction conditions for organic synthesis, providing valuable tools for optimising reactions and reducing the number of trials required. However, there are situations where running reactions under various conditions, altering things like the solvent, base, catalyst, or temperature, remains indispensable. Once such an array of reactions has been completed, it becomes necessary to acquire analytical data to experimentally measure the amounts of products, starting materials, and other components in the reaction. While LCMS offers a rapid method for gathering such data, it also presents a significant challenge in terms of processing and extracting useful information from the results so obtained. This is where Mnova’s automation engine (Mnova Gears, or simply Mgears) and the Chrom Reaction Optimization plugin come into play, offering a potential solution to these challenges. In this note, we explain how these tools can assist us in addressing these issues and discuss specific scenarios where they can be applied effectively.
The basic problem - finding the same components across a set of samples
The basic problem that needs to be solved in reaction optimisation or monitoring is to find the same set of components (typically starting materials, products, known side products) across a collection of LCMS files. This problem consists of two parts: the first, which is common to any automation process, is to find or somehow specify the relevant data to be operated on. The Mgears engine provides a solution to this part with several ways to select data. Do you need to search for data on a file share? Or listen for new data as it is generated? Or perhaps provide a list of files in a CSV? Or maybe you have an SMDS or need retrieval from a custom database? All these modes are supported in Mgears – not just for reaction optimisation, but for any similar automation. In most cases, the desired actions can be achieved through simple configuration options, such as clicking a checkbox to ‘find LCMS data’. In cases where the requirements are more exotic, the script engine can always come to the rescue to customise the behaviour according to the specific needs.
Providing multiple ways to define components
Once the data has been found, we must specify the components that require searching, and certain other options for analysis. Components can be defined in various ways: as a structure (mol file or SMILES string), a molecular formula, or simply as an m/z value. If you only have UV-based data, it is also feasible to define components solely according to their retention time. It is also possible to mix and match; in other words, you can potentially define certain components by mass, while others (such as those that do not ionise) can be defined exclusively by their retention time. This approach offers excellent flexibility, enabling the identification of components using the most suitable method for each individual case.
One problem that can arise is that of isomers. Perhaps you have two products with the same molecular weight. You can address this problem using an AND logic – defining a mass and a retention time range to ensure isomers are identified in a consistent manner.
Conclusions
Reaction optimisation is a critical step in developing efficient syntheses for final products or intermediates. While many approaches can be used to reduce the number of trial reactions, there is still a need to efficiently handle and analyse the generated LCMS data to quantify components. Mgears and Chrom Reaction Optimization provide a rapid, flexible, and configurable solution to this challenge, potentially saving laboratory scientists significant time. By providing efficient ways to locate data, define components, review results, address issues, and integrate with other systems, these tools streamline the analysis process and significantly enhance the productivity of research organisations.
4. Shimadzu: Rapid, Highly Sensitive and Direct Quantification of Fluticasone Propionate at Sub-pg/mL in Plasma Using LCMS-8060
- Application note
- Full PDF for download
User Benefits
- Rapid, simple and sensitive method with LLOQ of 0.2 pg/mL
- Single step sample extraction method increased sample productivity
Fluticasone propionate, a medium-potency synthetic corticosteroid is administered as nasal spray or drops for the treatment of allergic and non-allergic rhinitis; or by oral inhalation for the treatment of asthma. Therapeutic dose of fluticasone propionate results in very low plasma concentrations and requires a sensitive bioanalytical method for accurate quantification of the drug in plasma. Shimadzu Application Development Centre (ADC), Navi Mumbai has developed and validated the most sensitive method with lowest limit of quantification (LLOQ) of 0.2 pg/mL. The method has used a single step sample extraction technique and direction injection approach to eliminate environmental contamination. These factors enhance productivity of the pharmacokinetic investigation involving high-throughput analysis.
2. Salient Features
- A validated quantitative method was developed for the determination of fluticasone propionate in human plasma, in accordance with major US guidelines [1] . The results are presented in Table 1.
- The analytical throughput was enhanced using a rapid single-step extraction procedure and the ultra-fast technologies of the LCMS-8060 system.
- Optimization of the ionization and ion guide technologies led to improved ion production and transmission, enabling sensitive and selective quantification of fluticasone propionate down to 0.2 pg/mL.
- The plasma sample volume was carefully optimized to minimize wastage and extend the lifespan of the mass spectrometer.
- The chromatographic method was optimized to eliminate endogenous interference and reduce background noise for both the analyte and its deuterated internal standard.
4. Result and Discussion
4.1. Method Development
The initial experiments involved optimizing fluticasone propionate in both positive and negative ion ESI modes. In the positive ion mode, the [M+H]+ ion of fluticasone propionate at m/z 501.0 produced prominent product ions at m/z 293.05 with improved signal-to-noise ratio. The negative ion mode showed low signal-to-noise ratio of the product ion peak.
The internal standard (I.S.) displayed a molecular ion at m/z 506.0. The precursor ions (m/z 501.0 and 506.0) were introduced into the collision cell to generate the product ion spectrum. Both fluticasone propionate and fluticasone propionate-D5 exhibited a fragmentation pattern, with the base peak of the product ion spectrum observed at m/z 293.05 and 313.1. The highest abundance of the daughter ion was achieved with a collision energy of -20 eV. The transitions selected for monitoring fluticasone propionate and fluticasone propionateD5 were m/z 501.0→293.05 and 506.0→313.1, respectively.
To achieve the ultra-low detection limit of fluticasone propionate in human plasma, various HPLC columns and gradient programs were tested to optimize the response factor. Initial conditions were based on a prior LC-MS/MS method with an LLOQ of 1 pg/ml. Five different types of HPLC columns were evaluated during method development. However, Shim-pack GIST C18 column showed a higher response factor, improved sensitivity and better resolution. Analyte was eluted from the column under gradient flow.
The SPE process optimization focused on achieving maximum efficiency and recovery. Key steps included preconditioning the cartridge and washing with water. The concentration of organic solvents for washing and elution was adjusted, while testing various volumes and reconstitution solvents for optimal conditions. The ideal organic solvent percentages where 20% acetonitrile in water was used as a wash solution and 50% methanol was used as an eluent. The eluent was directly injected on LC-MS/MS for analysis.
5. Conclusion
LCMS-8060, along with special sample preparation provides best in class sensitivity for demanding bioanalytical assay of fluticasone propionate. The criticality of these assays is huge, both with respect to technical challenges and commercial impact for pharmaceutical organizations. By providing these ready to use solutions, we partner with your labs to achieve desired resultsin yourscientific endeavors.
5. Thermo Fisher Scientific: Decipher intricate glycoproteins using data-independent acquisition-proton transfer charge reduction and native top-down mass spectrometry
- Technical note
- Full PDF for download
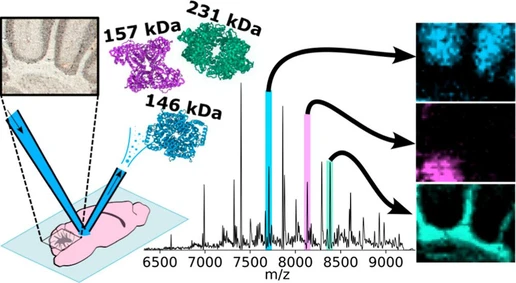
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic underscores the urgent need for rapid viral glycoprotein research. Viral glycoproteins, crucial for host cell attachment, are key targets for neutralizing antibodies produced by vaccines. While RNA sequencing reveals viral mutations, it does not capture post-translational modifications (PTMs) like glycosylation, which influence receptor binding and infection efficiency. A comprehensive understanding of glycoprotein glycosylation is essential for the development of effective vaccines and therapeutic strategies.
Native mass spectrometry (native MS or nMS) is a powerful tool in the mass spectrometry (MS) arsenal for characterizing glycosylation on viral glycoproteins. Unlike other methods, native MS maintains protein structures intact and introduces them into the mass spectrometer in a configuration that closely resembles their natural state in biological conditions. This technique provides an unaveraged snapshot of the solution conditions, allowing for the simultaneous detection of different proteoforms, such as varying glycosylations, which is challenging to achieve with other structural biology techniques. Native MS can identify both the number and types of glycoform compositions present.
However, challenges remain in native MS and native top-down MS characterization of glycoproteins as the heterogeneity leads to complex spectra. This study utilizes the high quadrupole mass filter coupled with proton transfer charge reduction (PTCR) on Thermo Scientific™ Orbitrap™ Tribrid™ platforms to decipher the complexity of glycoproteins, including ones from the COVID family using native MS.1-2 Top-down analysis employing electron transfer dissociation (ETD) provides structural, sequence, and PTM site information. In summary, the combination of data-independent acquisition-proton transfer charge reduction (DIA-PTCR) (Figure 1) and native top-down MS approaches enables a comprehensive characterization of viral glycoproteins.
Experimental
MS experiments
Glycoprotein analyses were performed on a Thermo Scientific™ Orbitrap™ Ascend Structural Biology Tribrid™ mass spectrometer. Native top-down analysis of human Fetuin was performed on a Thermo Scientific™ Orbitrap Eclipse™ Tribrid™ mass spectrometer.
Data analysis
The data were analyzed using Thermo Scientific™ BioPharma Finder™ 5.0 software.
Conclusions
- The extended quadrupole isolation range, reaching up to m/z 8,000, enhances isolation accuracy and S/N compared to ion trap isolation, thereby advancing native omics studies, as it not only works for top-down but for DIA-PTCR as well.
- Combining high quadrupole isolation with gas-phase charge reduction facilitates the rapid assessment of the MW of complex glycoproteins.
- DIA-PTCR streamlines the complete MW measurement process for glycoproteins.
- Native top-down analysis not only identifies the sequence but also unveils structural insights into glycoproteins such as hFet and RBD.
6. Waters Corporation: Quantification of Ergosterol Using Microwave-Assisted Extraction and a Rapid 5-Minute Isocratic HPLC Method
- Application note
- Full PDF for download
Benefits
- The CEM Discovery 2.0 microwave synthesizer allowed for a rapid, easy sample preparation that avoided saponification
- A rapid, 5-minute isocratic method reduced solvent consumption, leading to an overall greener method
- The Empower Software Peak Purity tool was utilized to confirm all peaks were well-separated in the final method
Functional mushrooms are a popular nutraceutical, with a variety of benefits being claimed for different fungal species. The numerous compounds contained in different species, coupled with the lack of guidelines in the supplement market, have contributed to the challenge in the development of quality analytical methods. Ergosterol is a compound that is common to all fungi and health benefits such as reduction in pain related inflammation, reduced incidences of cardiovascular disease, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-tumor activity have been reported.1-5 Additionally, ergosterol can act as a quality indicator, and can be used as a vitamin D2 supplement if it is exposed to UV light.6 Usage as a vitamin D2 supplement has been approved for certain foods, such as cereals, by the US FDA.7
Currently, there is a wide range of methods for the extraction and quantification of ergosterol in mushrooms. A variety of sample preparation methods have successfully extracted ergosterol, some of which include Soxhlet extractions, ultrasound-assisted, microwave-assisted, and supercritical fluid extractions. Most of these methods require a saponification step before the extraction, but some, such as microwave-assisted extractions, can achieve good results without using this long and tedious procedure.8
The work described here produced a rapid isocratic method able to separate and quantitate ergosterol from a variety of functional mushrooms. The ergosterol was extracted from mushroom samples using an optimized microwave-assisted extraction method. The ACQUITY 2998 PDA Detector was used to identify and quantify ergosterol in the mushroom samples. Spectral homogeneity of ergosterol was evaluated using the 3D PDA data coupled with the Peak Purity tool in Empower Software. A linear range was established and used to determine the concentration of ergosterol in the functional mushroom extracts.
Results and Discussion
An Arc Premier System with a gradient method was used for screening of both an XBridge Premier BEH C18 2.5µm x 4.6 x 50 mm and an XSelect Premier CSH™ C18 2.5µm x 4.6 x 50 mm Column. The XBridge BEH C18 Column provided a better separation and was used for further method development. Column screening was conducted with a 5-99%B gradient over 20 minutes. Initial screening conditions were able to produce a good separation that outperformed the resolution and tailing requirements of the desired method. Further method optimization consisted of improving the run time, peak tailing, and peak height.
Due to only having one analyte with no close-eluting compounds, isocratic elution methods were tested. Based on the screening runs, three isocratic methods were screened at 88%B, 89%B, and 90%B. The 88%B isocratic elution retained ergosterol long enough to be outside any baseline disturbances from the column front. The final elution can be seen in Figure 1. This method provided a resolution greater than 2.5 with a peak tailing factor of 1.0.
Conclusion
A fast method for the separation and determination of ergosterol content in mushrooms was developed utilizing an Arc Premier UHPLC System with PDA detection. A CEM Discovery 2.0 microwave synthesizer was used for rapid extraction while avoiding the lengthy saponification step. Empower Software’s Peak Purity tool, in combination with the 3D PDA spectrum collected, were able ensure the ergosterol to be spectrally pure. The linearity of the ergosterol allows for quantification within the expected ranges produced by mushrooms with this
extraction.