
KNAUER Eurokat Na Ion Exclusion/Ligand Exchange Columns
Analysis of sugar oligomers
The ionic form Na is best suited for the analysis of sugars oligomers up to a degree of polymerization (DP) of 8. It is a cation exchange material with 6 % cross linkage of the styrenedivinylbenzene copolymer. Best results are achieved with aqueous eluents, recommended eluent is pure deionized water. The usage of up to 10 % organic content in the mobile phase is possible.
Properties
- Polymer phase for the determination of sugar oligomers
- Na form, 6 % cross linkage
- Cation exchanger, extremly long lasting lifetime when correctly handled, best results with aqueous eluents, recommended eluent is pure deionized water, usage of up to 10 % organic content in the mobile phase is possible
Technical Data
- Sulfonated cross-linked styrenedivinylbenzene copolymer with 6 % cross linkage in the ionic form Na, available in 10 μm particle size, pressure stable up to maximum 100 bar
Recommended application areas
- Especially designed for the analysis of sugar oligomers, separates carbohydrates up to DP 8
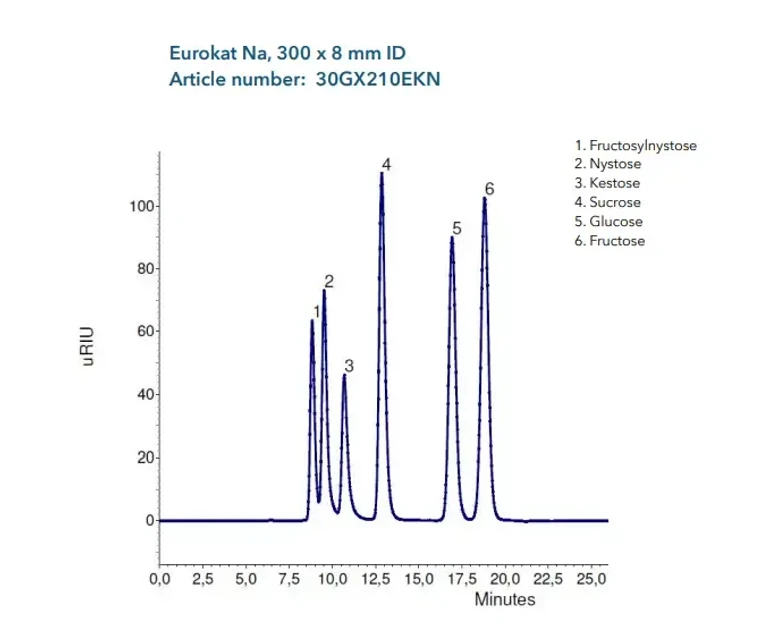 KNAUER: Eurokat Na Chromatogram
KNAUER: Eurokat Na Chromatogram
Tip: Eurokat columns are typically used with 100 % aqueous eluents. For storage, please avoid microbial growth by flushing the Eurokat column with 0.45 µm filtered ultrapure water and storing it at 4 °C.
KNAUER Ion Exclusion and Ligand Exchange Columns
Separation of organic acids, carbohydrates, alcohols on sulfonated cross-linked styrenedivinylbenzene copolymer
- Modifications
- Eurokat H
- Eurokat Ca
- Eurokat Pb
- Eurokat Na
- High Temperature Methods: Up to 90 °C
- Method Development: Optional up to 10 % organic solvent
- Chemically stable: pH 1–12
- Sustainability: Aqueous eluents protect the environment and are cost-effectiv
- User Friendly: Simple and robust methods for daily analysis. Versatile in its use.
- Simplicity: Easy purchase via our online store with fast delivery.
Characteristics
Eurokat high performance polymer phases were especially developed for the separation of organic acids, carbohydrates, alcohols and even complex mixtures of these compounds. Eurokat is a sulfonated cross-linked styrenedivinylbenzene copolymer available in several ionic forms (H, Ca and Pb). This particular cation exchanger is characterized by an outstanding density of functional groups, making it the ideal choice for your ion exclusion, size exclusion and ligand exchange chromatography.
Choice of chromatographic conditions
The Eurokat stationary phase is designed to be applicable to a wide range of diverse chromatographic conditions. All Eurokat columns can be used at temperatures up to 90 °C with no organic solvents. The best separation of sugars can be achieved using between 60 to 90 °C. To extend separation performance, it is possible to connect up to three columns of Eurokat in series. Eurokat columns require no organic solvents and thus are environmentally friendly.
Stability
Eurokat polymer columns are extremely stable over the whole pH range. This is one striking advantage compared with silica-based phases which have a limited lifetime at pH extremes, especially in the higher pH range. Most importantly, Eurokat phases show extraordinary column lifetime stability and are not affected by aqueous solvents.
Application areas
- Carbohydrates and organic acids in softdrinks and fruit juices
- Sugar substitutes
- Food preservatives
- Dairy products
- Urine analytic (Uric acid, Hippuric acid)
- Monitoring of fermentation processes
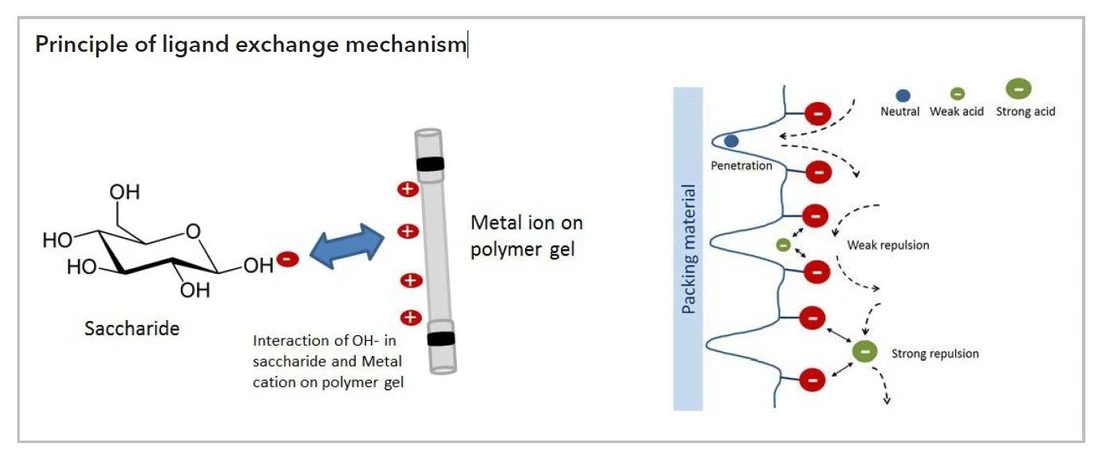 KNAUER: Eurokat - Principle of ligand exchange mechanism
KNAUER: Eurokat - Principle of ligand exchange mechanism


